ROS Commands – ROS Topic
After describing “rosnode” command in previous blog, now we will discuss another important ROS command which is about “topic”. Since topic is a very important concept. To understand these commands you should be familiar with the “topic” concept. If you haven’t already familiar with it, please read ROS Terminologies and ROS Message Communication blogs.
“rostopic” command
The “rostopic” command is used to get the information about the topics and to print and publish the message with the specific topic name. Before exercising the commands, we will see what arguments are used with “rostopic” command.
Run the following command.
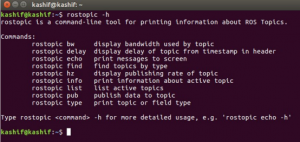
rostopic -h
In the figure below we can see number of commands. Each argument along with “rostopic” basically acts as a new command.
To exercise these commands, close all previously running nodes/terminals, and open three new terminals. Run following three commands on all three terminals separately.
Run in Terminal 1
roscore
Run in Terminal 2
rosrun turtlesim turtlesim_node
Run in Terminal 3
rosrun turtlesim turtle_teleop_key
Let’s exercise the commands.
“rostopic list” command
The “rostopic list” command is used to show the list of active topics.
Open a new terminal (say Terminal 4) and run the command
rostopic list
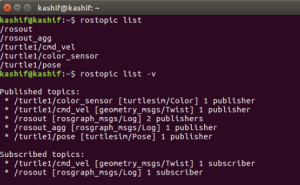
you will see the list of following topics
—
/rosout
/rosout_agg
/turtle1/cmd_vel
/turtle1/color_sensor
/turtle1/pose
—
If we add the ‘-v’ option to the “rostopic list” command, it separates the published topics and the subscribed topics. In addition, it shows the message type for each topic.
Run in Terminal
rostopic list -v
The results in the terminal for above both commands are shown in figure below
“rostopic echo” command
The “rostopic echo” command print the content of a message on screen for a specific topic.
The structure of the command is as follows
rostopic echo [Topic_Name]
We will see later what type of a message is communicated through the topic. Here we will just execute this command and see the results.
The topic name is “/turtle1/pose”. We have already seen this topic in active topic list.
Run the command
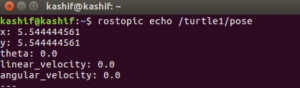
rostopic echo /turtle1/pose
In figure below it shows the data for ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘theta, linear_velocity’, and ‘angular_velocity’ that constitutes the ‘/turtle1/pose’ topic in real-time.
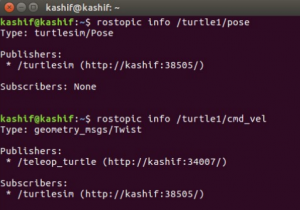
“rostopic info” command
The “rostopic info” command is used to get the information about a particular topic. The structure of this command is as follows
rostopic info [Topic_Name]
Run the command to see the information about the “/turtle1/pose” topic.
rostopic info /turtle1/pose
Also, run the command to see the information about “turtle1/cmd_vel” topic.
rostopic info /turtle1/cmd_vel
Result of executing both commands is shown in figure below
“rostopic pub” command
Most of the time, we define publisher node in program, which publish the data periodically on a specific topic, and the subscriber node receives it. However, we also have the command “rostopic pub” to directly publish the message on command prompt with the specific topic name
The structure of the command is as follows
rostopic pub [Topic_Name] [Message_Type] [Parameter]
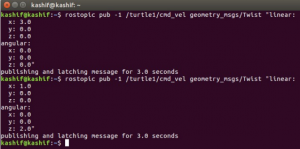
Now we publish a message with the topic name “/turtle1/cmd_vel” with a message type of “geometry_msgs/Twist”.
rostopic pub -1 /turtle1/cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist -- '[3.0, 0.0, 0.0]' '[0.0, 0.0, 0.0]'
We run this command again with different values
rostopic pub -1 /turtle1/cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist -- '[1.0, 0.0, 0.0]' '[0.0, 0.0, 2.0]'
Here “-1” means the data will be published once.
linear parameter means that the object (in this case turtle) will move in x, y, or z direction with give speed, and angular parameter means, the object will rotate about x, y, or z –axis with specified speed.
(For example in first example the movement will be in x direction with the speed of 3.0 m per second, and in second example the movement will be with the speed of 1.0 m per second in the direction of x, and a rotation of 2 rad per second in around z-axis)
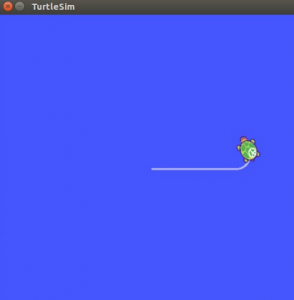
The figure below shows the execution of the commands and another image shows the movement of turtle after execution of the commands.
Since the turtle has subscribed the topic “turtle1/cmd_vel” of message type “geometry_msgs/Twist”, the turtle moved accordingly after receiving the published data values as shown below