ROS Basics 03 – Topic: Subscriber
In previous blog, we have created and run a publisher node that is continuously publishing an integer type message on a topic. In this blog we will learn how to create a subscriber node that subscribes to the topic and uses the received message.
Subscribing to a Topic
Since we have already created a package “ ros_basics” in which python file for publisher node was created. We will create the python file for subscriber node in the same package.
To go to the package open the terminal and run the command
roscd ros_basics
Go to src folder using following command
cd src
Run the command to check contents of the folder
ls
We can see that the file “topic_publisher.py” is already there.
Now create another file “topic_subscriber.py”
Run command
touch topic_subscriber.py
Assign execution permission to the file
chmod +x topic_subscriber.py
Again see the contents of the file
Run command
ls
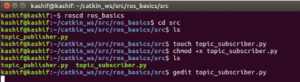
you can see that now there are two files “topic_publisher.py” and “topic_subscriber.py” in the folder as show in figure below.
Now we will modify the file “topic_subscriber.py”
Run the command
gedit topic_subscriber.py
Copy and paster following code into the file
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import Int32
def callback(msg):
print msg.data
rospy.init_node('topic_subscriber')
sub = rospy.Subscriber('counter', Int32, callback)
rospy.spin()
All above executed commands are shown in figure below
The python program file “topic_subscriber.py” will look like as shown below
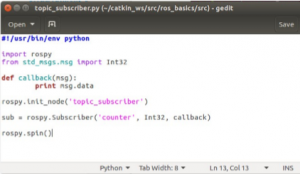
Save and close the file.
Run Subscriber Node
Now we execute the file using “rosrun” command. Remember the command can be run from any directory, however its structure will remain the same as already described.
However, first ensure that “roscore” and publisher_node is already running
For this open a new terminal and run the command
roscore
Open another terminal and run the command (To run the publisher node)
rosrun ros_basics topic_publisher.py
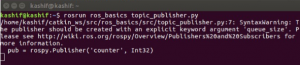
We can see that publisher node is running as show in figure below
Now run in a new terminal (To run subscriber node)
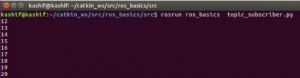
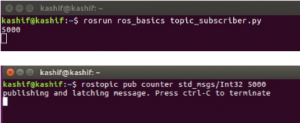
rosrun ros_basics topic_subscriber.py
You will see that the subscriber node started receiving and displaying the message (which is of Integer type) as shown in figure below
In a new terminal we can run several commands to see the information about nodes, topics, messages etc.
For example we can check the list of nodes and topics currently running
run in a terminal
rosnode list
Also run
rostopic list
You can further get the information about topic and message as show in figure below
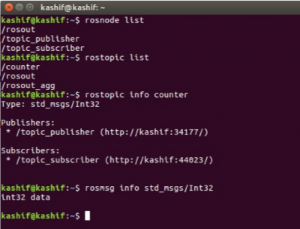
Note: In order to get the information about message, you will have to give both package name (such as “std_msgs”) and message type (such as “Int32”).
The command will look like
rosmsg info std_msgs/Int32
You can also write above command as follow
rosmsg show std_msgs/Int32
It will do the same thing
Writing on the Topic using Command Line
Suppose publisher node is not running, but only subscriber node is running. If we want to send data to subscriber node, we can directly do it using “rostopic pub” command.
Close all terminals except where “roscore” is running
Now open a terminal and run the command
rosrun ros_basics topic_subscriber.py
(It will initiate subscriber node)
Open an other terminal and run the command
rostopic pub counter std_msgs/Int32 5000
This command will publish “5000” on the topic counter.
You can see that the subscriber node receives the message (value 5000) and displayed it.
Explaining the Python Program File
Now we will explain the code. However, we will skip the code lines that we have already explained in previous blog
The Code is
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import Int32
def callback(msg):
print msg.data
rospy.init_node('topic_subscriber')
sub = rospy.Subscriber('counter', Int32, callback)
rospy.spin()
In case of subscriber node, the important part of the code is “callback” function. Once a node is subscribed to a topic, then every time when a message is received, the callback function is called. The received message is passed as a parameter to the “callback” function.
As we can see the line
sub = rospy.Subscriber(‘counter’, Int32, callback)
the node is subscribed with the arguments topic (counter), message type (Int32) and the callback function.
In the definition of “callback” function only one thing is being performed that is to print the received data as can be seen in following lines
def callback(msg):
print msg.data
The last line “rospy.spin()” is added so that the subscriber node continue running.

